- Blenders, Mixers, & Agitators
- Tri Clamp Mixers
- Top Entry Mixers
- High Viscosity Mixers
- Mag Drive Mixers
- Explosion Proof Mixers
- Sanitary Mixers
- Single Use Mixers & Agitators
- Bottom Entry Mixers
- Carboy Mixers
- Corrosion Resistant Mixers & Mixing Tanks
- Industrial Mixers
- Blenders & Shakers
- Industrial Mixing Accessories
- Sanitary & Industrial Mixing Impellers
- Mixing Tanks & Engineered Systems
- Mechanical Seals
- Applications
The Ultimate Guide to Jacketed Mixing Tanks for Efficient Mixing Solutions
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial mixing, the significance of a jacketed mixing tank cannot be overstated. These specialized tanks play a crucial role in ensuring homogeneous mixtures in various industries, ranging from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and chemicals. According to a 2020 report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for mixing equipment, including jacketed mixing tanks, is projected to reach USD 12.34 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.5%. This growth is driven by increased demand for efficient mixing processes that enhance product quality and reduce operational costs.
Jacketed mixing tanks are particularly valued for their ability to maintain precise temperature control during mixing operations. This attribute is essential for applications requiring heat transfer, such as those involving sensitive ingredients or processes that require specific thermal conditions. The same MarketsandMarkets report underscores that temperature-controlled mixing not only improves product consistency but also extends shelf life and optimizes energy consumption, ultimately leading to more sustainable manufacturing practices. As industries strive for greater efficiency and productivity, understanding the complexities and functionalities of jacketed mixing tanks will empower manufacturers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
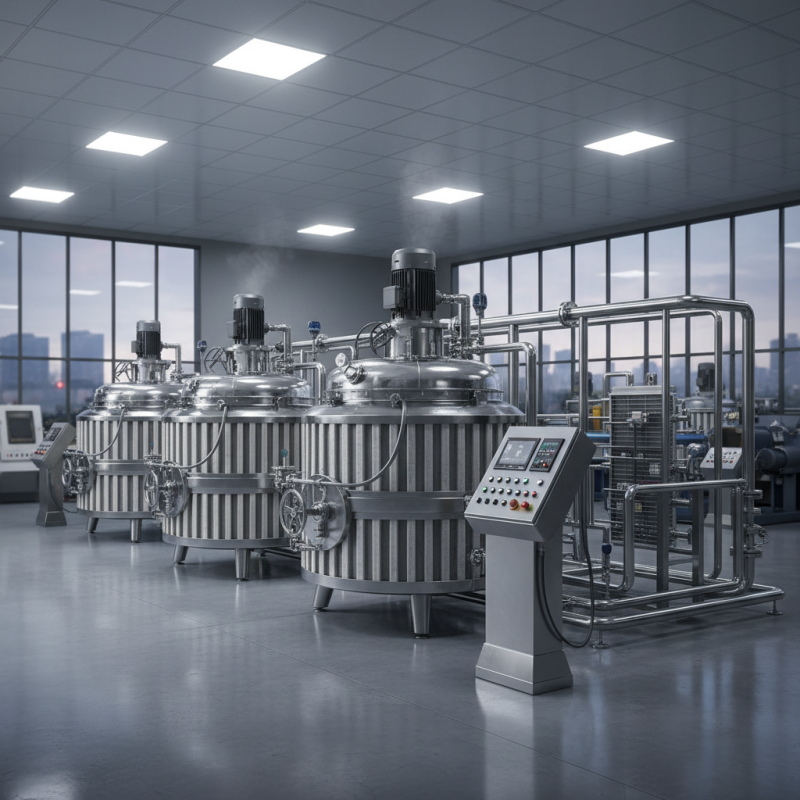

Understanding Jacketed Mixing Tanks: Definition and Purpose
Jacketed mixing tanks are specialized vessels designed to facilitate efficient mixing processes while maintaining optimal temperature control. These tanks feature an outer jacket that encases the mixing chamber, allowing for the circulation of heating or cooling fluids. This design is particularly beneficial in industries where temperature-sensitive materials need to be processed, such as food production, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. By providing a controlled environment, jacketed mixing tanks ensure uniform mixing, enhance product consistency, and minimize the risk of thermal degradation.
The purpose of a jacketed mixing tank goes beyond mere mixing; it also addresses the critical aspect of thermal management during the mixing process. For instance, when combining materials that have different thermal properties, managing the temperature helps maintain the integrity of the final product. The ability to heat or cool the contents simultaneously while mixing allows for greater flexibility in production schedules and reduces the time required for processing. Ultimately, the integration of temperature control features in mixing tanks leads to improved efficiency and quality in various manufacturing processes.
Key Components of Jacketed Mixing Tanks and Their Functions
Jacketed mixing tanks are essential for achieving efficient mixing solutions, primarily due to their unique design and key components. One of the most critical parts is the jacket itself, which serves as an insulating layer that surrounds the tank. This jacket facilitates temperature control by allowing a circulating medium—such as water, steam, or oil—to maintain the desired thermal conditions within the tank. This is particularly advantageous in processes requiring precise temperature management, like the mixing of temperature-sensitive ingredients.
Another vital component is the mixing impeller, which performs the primary task of blending materials. Various types of impellers can be used depending on the specific application, including high-shear, axial-flow, or radial-flow designs. The choice of impeller affects the mixing efficiency and uniformity, making it crucial to select the right one for the material properties involved. Additionally, the tank’s structure may include baffles that help disrupt the flow patterns, enhancing the mixing process by preventing vortex formation and ensuring an even distribution of materials.
A further important aspect is the tank’s outlet and inlet configurations, designed to facilitate easy loading and unloading of materials while minimizing contamination risks. Some tanks are equipped with sight glasses, allowing operators to monitor the mixing process visually. Overall, the design and components of jacketed mixing tanks play a significant role in ensuring effective and controlled mixing, catering to the needs of various industrial processes.
The Ultimate Guide to Jacketed Mixing Tanks: Key Components and Their Functions
This bar chart displays the efficiency and functionality of key components in jacketed mixing tanks, highlighting their importance in achieving optimal mixing solutions.
Advantages of Using Jacketed Mixing Tanks in Various Industries

Jacketed mixing tanks are essential tools across various industries, offering significant advantages in terms of temperature control and efficient mixing. These tanks feature a dual-layer structure that allows for the circulation of heating or cooling fluids, enabling precise temperature management for sensitive products. In food processing and pharmaceuticals, for instance, maintaining an optimal temperature is critical to preserving the integrity and quality of ingredients. By integrating jacketed mixing tanks, businesses can ensure consistent product results while enhancing overall process efficiency.
Tips: When selecting a jacketed mixing tank, consider the specific heating or cooling requirements of your application. Understanding the viscosity and characteristics of the materials being mixed is also crucial, as it will influence the design and scale of your tank. Additionally, ensure that the materials used in the tank construction are compatible with your processes to prevent contamination.
The versatility of jacketed mixing tanks extends to industries such as chemicals, cosmetics, and coatings. In these sectors, the ability to control temperature during chemical reactions can significantly impact product yield and quality. By employing jacketed mixing technology, companies can expedite processes, reduce energy costs, and enhance workplace safety through better thermal management. Therefore, the investment in jacketed mixing tanks often leads to a more streamlined production workflow and higher customer satisfaction.
Tips: Regular maintenance of jacketed mixing tanks is vital to safeguard their performance. Ensure that the jacket system is regularly inspected for leaks, and evaluate the insulation to maintain energy efficiency. Keep a detailed record of maintenance checks to ensure compliance and optimal functioning.
Best Practices for Operating and Maintaining Jacketed Mixing Tanks

Operating and maintaining jacketed mixing tanks effectively is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. One of the best practices involves regularly inspecting the heating and cooling jackets, as they are vital for maintaining precise temperature control during the mixing process. Any inconsistencies in heating or cooling can lead to product inconsistencies and may cause damage to the tank. It's advisable to schedule routine maintenance checks, focusing on the integrity of seals and gaskets to prevent leaks and ensure efficient heat transfer.
Another important aspect is the calibration of mixing speed and duration based on the specific requirements of the materials being processed. Initiating the mixing at a lower speed and gradually ramping up allows for a more consistent blend, reducing the likelihood of aeration or damage to delicate components. Additionally, operators should keep thorough records of mixing parameters and maintenance activities, which can lead to improved operational efficiency and help identify any recurring issues that may arise over time. Regular training for operators on these best practices is also essential, ensuring that the team is well-versed in the correct procedures for operating these complex systems.
Choosing the Right Jacketed Mixing Tank for Specific Applications
When selecting a jacketed mixing tank, it's essential to consider the specific application to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Different industries, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, have unique requirements that influence the choice of material, size, and design of the tank. For instance, while food-grade stainless steel may be ideal for food applications due to its hygienic properties, glass-lined tanks might be preferred in certain chemical environments to prevent contamination. Understanding the material compatibility and regulatory standards pertinent to your industry is crucial for making the right choice.
Another critical factor in selecting a jacketed mixing tank is the tank's size and capacity, which should align with production needs. Evaluating current and future production volumes helps determine the optimal tank size, preventing bottlenecks in the mixing process. Additionally, the tank design, which includes elements like impeller type, heat transfer requirements, and insulation, plays a significant role in achieving efficient heat control and mixing uniformity. By properly assessing these variables, businesses can select a jacketed mixing tank that not only meets their specific application needs but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
The Ultimate Guide to Jacketed Mixing Tanks for Efficient Mixing Solutions
| Tank Size (Gallons) | Material | Jacket Type | Heating Method | Mixing Speed (RPM) | Application Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | Stainless Steel | Full Jacket | Steam | 50 | Food Processing |
| 200 | Carbon Steel | Half Jacket | Hot Water | 75 | Chemical Mixing |
| 300 | Stainless Steel | Full Jacket | Electric | 100 | Pharmaceuticals |
| 500 | Mild Steel | Double Jacket | Thermal Oil | 60 | Cosmetics |
Related Posts
-

10 Best Chemical Mixing Tanks for Optimal Performance in 2023
-

How to Choose the Right IBC Storage Tank for Your Needs
-
Why Jacketed Stainless Steel Tanks Are Essential for Food Processing Operations
-
2025 Guide: How to Use a 275 Gallon IBC Tote Tank Effectively
-

2025 Top PE Tank Features Benefits and Uses for Your Projects
-

2025 Top 10 Uses for 275 Gallon IBC Tote Tanks You Need to Know
